Warm up
Copy and complete the following sentence by selecting one of the bold words:
In musical instruments, low notes are created by making the string or tube longer or shorter, or by making it thicker or thinner.
Today’s videos
What is sound?
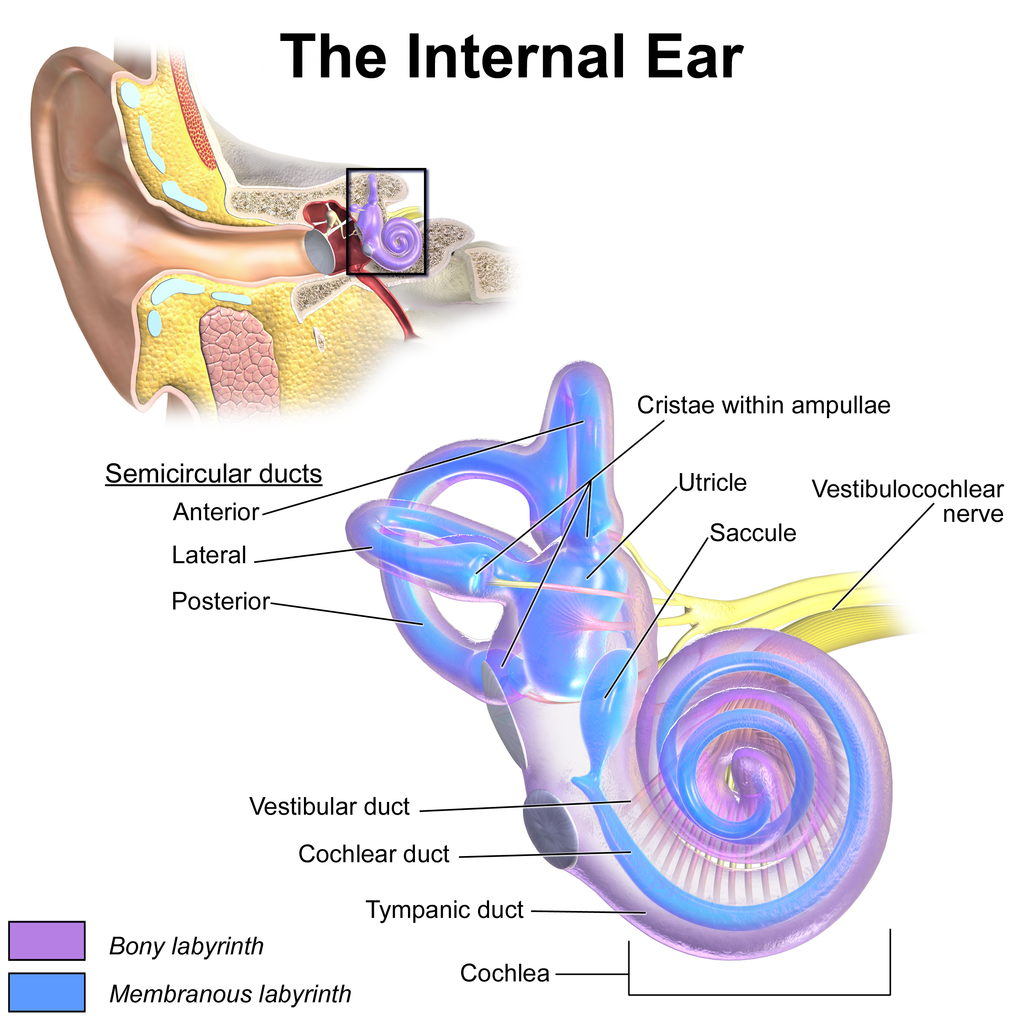
How does sound travel
Highlights from videos
What is sound

- Compression: Areas where atoms/molecules are squeezed closer together (have more elastic energy).
- Rarefaction: Areas where molecules are spread apart (have less elastic energy).
- Hz (short for Hertz, like the rental car company) is a measure of the frequency: 1 cycle every second = 1 Hz. An example in sound: 440 Hz is the note “A.”
- The medium is the substance the waves travel through. The medium moves only a short distance; it’s the energy that moves the entire distance from the source of the wave to whatever receives that energy (e.g. from a speaker to your ear).
How does sound travel
This video starts with a thought experiment. Thought experiments are experiments we can’t actually do, but by thinking about that situation, it helps us to understand. By looking at a super-long bar of metal, we can ‘slow down’ sound.
- Wave motion can be thought of as a chain reaction of one portion moving the portion next to it.
- Sound waves are particles bouncing into each other
- Particles only travel a short distance
- Speed of sound depends on the material the medium is made up of.
- Sound waves are not objects, they are the movement of energy.